Table of Contents
ToggleAre you new to the world of SaaS (Software as a Service)? Or have you been in the industry for a while but still struggle with the terminology?
Don’t worry, you’re not alone! With the fast-paced evolution of technology, new concepts and terms are constantly emerging, making it difficult to keep up.
To stay ahead of the curve and understand the ins and outs of SaaS, it’s crucial to have a good grasp on its terminology. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the key concepts and definitions you need to know to navigate the world of SaaS with confidence.
Whether you’re a business owner, IT professional, or simply curious about the industry, this guide will provide you with a solid foundation of SaaS terminology, so you can speak the language fluently and excel in your field. So, let’s dive in!
The importance of understanding SaaS terminology
In the world of SaaS, a vast array of technical terms and jargon can be confusing for the uninitiated. However, having a good understanding of SaaS terminology is essential for anyone who wants to succeed in this field.
For example, understanding the difference between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS can help you decide which cloud computing services to use for your business needs. Similarly, knowing what SLA, uptime, and scalability mean can help you get the most value from your SaaS subscription.
Additionally, having a good grasp of SaaS terminology can help you communicate more effectively with colleagues, vendors, and customers and make it easier to collaborate and innovate.
Taking the time to learn and understand SaaS terminology is a crucial step toward becoming a successful player in the fast-moving world of cloud computing.
Key Concepts and Definitions
SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a cloud-based delivery model in which software applications are hosted and provided to users over the internet. SaaS allows users to access software applications from any device with an internet connection without downloading or installing anything locally.
PaaS, or Platform as a Service, is another cloud-based delivery model in which developers can build, test, and deploy custom applications on a cloud platform without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure.
IaaS, or Infrastructure as a Service, is a cloud-based delivery model where users can rent virtualized computing resources from a cloud provider, such as servers, storage, and networking.
SLA, or Service Level Agreement, is a contract between a SaaS provider outlining the quality and reliability the provider delivers will deliver. SLAs typically include metrics such as uptime, response time, and support availability.
Uptime time of the time that a SaaS application is available and operational. High uptime is essential for ensuring users can access the application whenever needed.
Scalability refers to a SaaS application’s ability to handle several users or a growing workload without performance degradation. A scalable application can grow seamlessly with the needs of the business without requiring significant infrastructure changes.
SaaS Fundamentals
SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a cloud-based delivery model in which software applications are hosted and provided to users over the internet. Unlike traditional software models where users must purchase and install software on their hardware, SaaS allows users to access applications through a web browser or mobile app, typically on a subscription basis.
This model offers several benefits, including lower upfront costs, automatic updates, and scalability. Additionally, SaaS providers take care of software maintenance, security, and infrastructure, freeing users to focus on their core business activities.
Famous examples of SaaS applications include Salesforce for customer relationship management, Zoom for video conferencing, and Dropbox for file sharing and storage. SaaS has revolutionized how businesses access and use software, enabling greater efficiency, flexibility, and cost savings.

SaaS and its key characteristics
SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a cloud-based delivery model in which software applications are hosted and provided to users over the internet. Several key characteristics of SaaS distinguish it from traditional software delivery models.
- Firstly, SaaS applications are typically accessed through a web browser or mobile app, with users logging in to a centralized platform to access the software. This eliminates the need for users to install and maintain software on their hardware.
- Secondly, SaaS is typically provided on a subscription basis, with users paying a monthly or annual fee to access the software. This pricing model offers greater flexibility and lower upfront costs than traditional software purchases.
- Thirdly, SaaS providers maintain the software, including updates, security, and infrastructure. This frees users to focus on their core business activities rather than spending time and resources on software maintenance.
- Fourthly, SaaS applications are highly scalable, meaning they can handle a growing number of users and workloads without requiring significant infrastructure changes. This makes it easy for businesses to add or remove users as needed without worrying about the underlying technology.
SaaS is a powerful delivery model that offers several advantages over traditional software delivery methods, including lower costs, greater flexibility, and improved scalability.
Comparison to traditional software models
SaaS, or Software as a Service, offers several key advantages compared to traditional software models.
- Firstly, traditional software models often require users to purchase and install software on their hardware, which can be time-consuming and expensive. In contrast, SaaS applications are accessed through a web browser or mobile app, eliminating users needing to install and maintain software on their hardware.
- Secondly, traditional software models typically require users to pay a significant upfront cost to purchase the software, which can be a substantial barrier to entry for small businesses. In contrast, SaaS is typically provided on a subscription basis, with users paying a monthly or annual fee to access the software. This pricing model offers greater flexibility and lower upfront costs than traditional software purchases.
- Thirdly, traditional software models often require users to handle software maintenance and update themselves, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. In contrast, SaaS providers maintain the software, including updates, security, and infrastructure. This frees users to focus on their core business activities rather than spending time and resources on software maintenance.
- Fourthly, traditional software models may need help to keep up with changing technology and user needs, leading to software becoming obsolete over time. In contrast, SaaS applications are highly scalable, meaning they can handle a growing number of users and workloads without requiring significant infrastructure changes. This makes it easy for businesses to add or remove users as needed without worrying about the underlying technology.
SaaS offers several advantages over traditional software models, including lower costs, greater flexibility, improved scalability, and reduced maintenance requirements.
Business Metrics
Business metrics are essential for measuring the performance and success of a SaaS business. There are several key metrics that SaaS companies should track to ensure they are meeting their business goals and making informed decisions.
- Firstly, Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) is a crucial metric for SaaS businesses, providing insight into the monthly recurring revenue generated. MRR considers the number of customers, the subscription fees, and any changes in subscription plans.
- Secondly, Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a crucial metric for measuring the cost-effectiveness of acquiring new customers. CAC considers the total cost of acquiring a customer, including marketing, sales, and other related expenses.
- Thirdly, Churn Rate is a metric that measures the rate at which customers cancel their subscriptions. A high churn rate can indicate issues with product quality, customer support, or other factors that must be addressed.
- Fourthly, Lifetime Value (LTV) is a metric that measures the total revenue generated by a customer over the entire length of their relationship with the company. This metric is essential for understanding the long-term value of each customer and can help inform marketing and sales strategies.
- Finally, Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a metric that measures customer satisfaction and loyalty. NPS is calculated based on customer responses to a question: “How likely are you to recommend our product to a friend or colleague?” This metric can provide valuable insights into a SaaS business’s overall health and help identify improvement areas.
Tracking these and other key metrics is essential for understanding the performance and success of a SaaS business and making informed decisions to drive growth and profitability.

ARR, MRR, CARR, and their importance in measuring SaaS business performance
ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue), MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue), and CARR (Contracted Annual Recurring Revenue) are essential metrics for measuring the performance and growth of a SaaS business.
- ARR is the total revenue a SaaS business generates from annual subscriptions. ARR is calculated by multiplying the full yearly subscriptions by the subscription fee. This metric is important because it provides a high-level view of the company’s overall performance and growth.
- MRR, on the other hand, is the total amount of revenue a SaaS business generates from monthly subscriptions. MRR provides a more granular view of revenue and is calculated by multiplying the total number of monthly subscriptions by the subscription fee.
- CARR is the total revenue a SaaS business generates from its existing customer contracts. This metric considers any renewals or upgrades to the agreement, providing insight into the company’s expected income over the long term.
These metrics are essential for understanding the recurring revenue generated by a SaaS business and its growth potential. They provide valuable insights into the company’s financial health and help inform decision-making around pricing, product development, and sales strategies.
By tracking ARR, MRR, and CARR, SaaS businesses can identify trends and patterns in revenue growth and make informed decisions about how to scale their business. For example, if ARR is increasing, but MRR is stagnant, the company may need to focus on improving its sales processes to attract more monthly subscribers. Alternatively, if CARR is decreasing, the company may need to focus on improving customer retention and renewals.
ARR, MRR, and CARR are essential metrics for measuring the performance and growth of a SaaS business, providing valuable insights into the company’s recurring revenue and potential for long-term success.
Churn and its impact on SaaS revenue growth
Churn is a crucial metric for SaaS businesses, measuring the rate customers cancel their subscriptions. High churn rates can significantly impact growth and the overall success of a SaaS business.
When customers churn, they no longer pay for the product or service. This can result in a loss of revenue and increased costs associated with acquiring new customers to replace those who have churned. In addition, high churn rates can damage the company’s reputation, making it more challenging to attract new customers and grow the business.
Reducing churn is essential for SaaS businesses seeking long-term growth and success. Several strategies can be used to reduce churn, including improving product quality and customer support, offering incentives for customers to remain subscribed, and providing regular updates and new features to keep customers engaged.
SaaS businesses can achieve higher revenue growth and greater profitability over time by reducing churn. This is because it is often less expensive to retain existing customers than it is to acquire new ones. In addition, reducing churn can improve the company’s reputation and increase customer loyalty, leading to more referrals and positive reviews.
Churn is a critical metric for SaaS businesses, and reducing churn rates should be a key priority for companies looking to achieve long-term success and growth.
TAM and SAM and their role in market sizing
TAM (Total Addressable Market) and SAM (Serviceable Available Market) are key metrics used in market sizing for SaaS businesses.
- TAM represents the total demand for a product or service in a given market, assuming that all potential customers would be interested in purchasing the product or service. TAM is typically calculated based on the size of the overall market, the number of potential customers, and the potential revenue that could be generated.
- However, SAM represents the portion of the TAM that a particular company or product can realistically target and serve. SAM considers factors such as competition, market share, and other market dynamics that may impact a company’s ability to capture a specific portion of the overall market.
By calculating TAM and SAM, SaaS businesses can gain valuable insights into their market’s potential size and growth and the opportunities and challenges they may face in capturing a portion of that market. These metrics inform product development, pricing strategies, and sales and marketing efforts, ensuring that the company targets the right customers and maximizes revenue potential.
TAM and SAM are critical metrics for SaaS businesses, providing valuable insights into market sizing and growth potential. By understanding these metrics and how they relate to their business, SaaS companies can make informed decisions that drive growth and success over the long term.

Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing drive growth and success in the SaaS industry. Here are some key concepts and strategies to keep in mind:
- Firstly, effective targeting is critical for successful sales and marketing in SaaS. SaaS businesses should identify their ideal customer profile and target their sales and marketing efforts accordingly. This may involve using customer data to understand buyer personas and develop targeted messaging and campaigns.
- Secondly, lead generation is a crucial aspect of SaaS sales and marketing. Lead generation strategies can include content marketing, social media advertising, email marketing, and other tactics designed to attract and engage potential customers.
- Thirdly, a strong sales funnel is essential for converting leads into paying customers. This may involve developing a transparent sales process, providing demos or trials, and using sales enablement tools to help sales teams close deals.
- Fourthly, customer retention is critical for driving long-term growth and profitability in SaaS. SaaS businesses should prioritize customer success and support, providing regular updates, new features, and responsive customer service to keep customers engaged and satisfied.
- Finally, data and analytics are essential for measuring the effectiveness of sales and marketing efforts. SaaS businesses should track metrics such as conversion rates, churn rates, and customer lifetime value to inform decision-making and identify areas for improvement.
Effective sales and marketing strategies drive growth and success in the competitive SaaS industry. By prioritizing targeting, lead generation, sales funnel development, customer retention, and data and analytics, SaaS businesses can attract and retain customers, maximize revenue potential, and achieve long-term success.
Lead generation and its importance in driving SaaS business growth
Lead generation is critical to driving growth and success in the SaaS industry. By generating steady high-quality leads, SaaS businesses can attract and engage potential customers, build brand awareness, and drive revenue growth.
- Effective lead generation involves a range of strategies and tactics, including content marketing, social media advertising, email marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO). These tactics are designed to attract potential customers to the business, educate them about the product or service, and ultimately convince them to take action and become paying customers.
- The importance of lead generation in SaaS cannot be overstated. By generating a constant stream of fresh leads, SaaS businesses can increase their chances of converting those leads into paying customers, maximizing revenue potential, and achieving long-term success. Without a steady flow of new information, it is difficult for SaaS businesses to grow and succeed in the competitive marketplace.
- In addition, effective lead generation can help SaaS businesses identify and target their ideal customer profile, allowing them to focus their sales and marketing efforts more effectively. By understanding the needs and preferences of potential customers, SaaS businesses can tailor their messaging and campaigns to better resonate with those customers and drive higher conversion rates.
Lead generation is essential for driving growth and success in the SaaS industry. By prioritizing effective lead generation strategies and tactics, SaaS businesses can attract and engage potential customers, build brand awareness, and drive revenue growth and long-term success.
Sales funnel and its key stages
A sales funnel a visual representation of the steps a potential customer goes through to become a paying customer. There are typically four critical stages in a sales funnel:
- Awareness: In this stage, potential customers become aware of the product or service through marketing and advertising. This may include social media ads, blog posts, or other content marketing efforts.
- Interest: Once potential customers become aware of the product or service, they may become interested in learning more. This stage may involve providing more information about the product or service, such as through a website or a demo.
- Decision: In the decision stage, potential customers evaluate the product or service and decide whether to purchase it. This may involve a free trial or a consultation with a sales representative.
- Action: In the final stage of the sales funnel, potential customers decide to purchase the product or service and become paying customers.
By understanding the critical stages of the sales funnel, SaaS businesses can develop effective sales strategies tailored to each location. This may involve providing educational content during the awareness stage, offering demos or free trials during the interest stage, providing detailed product information during the decision stage, and offering incentives or discounts to encourage action.
A well-designed sales funnel essential for converting potential customers into paying customers and driving growth and success in the SaaS industry. By understanding the critical stages of the sales funnel and tailoring sales strategies accordingly, SaaS businesses can maximize their chances of success and achieve long-term growth and profitability.

Inbound and outbound marketing and their differences
Inbound and outbound marketing are two distinct marketing strategies in the SaaS industry.
- Inbound marketing is a strategy that focuses on attracting potential customers through targeted content marketing and lead-generation efforts. This may include techniques such as blogging, social media marketing, search engine optimization (SEO), and email marketing.
Inbound marketing aims to create content that potential customers find useful or interesting and to use that content to attract potential customers to the company’s website or other online channels. Once potential customers have engaged with the content, they may become paying customers. - On the other hand, outbound marketing is a strategy that focuses on reaching out to potential customers through more traditional marketing channels such as cold calling, direct mail, or paid advertising. Outbound marketing aims to reach a broad audience and generate leads through more natural means, such as offering promotions or discounts.
While both inbound and outbound marketing can effectively generate leads and drive revenue growth, they differ in several ways. Inbound marketing is more cost-effective and targeted, focusing on attracting potential customers who have already expressed an interest in the product or service. On the other hand, outbound marketing can be more expensive and less targeted, as it involves reaching out to a broader audience to generate leads.
The choice between inbound and outbound marketing will depend on the specific goals and needs of the SaaS business. While inbound marketing can be effective in building a solid brand and attracting engaged leads, outbound marketing may be more effective for generating leads quickly or reaching a broader audience.
By understanding the differences between these two marketing strategies, SaaS businesses can make informed decisions about how to allocate their marketing budgets and drive growth and success over the long term.
PPC advertising and its role in SaaS marketing
PPC (Pay-Per-Click) advertising is a crucial strategy for driving growth and success in the SaaS industry. PPC advertising involves placing ads on search engines or social media platforms and paying a fee each time a user clicks on the ad.
PPC advertising can be a highly effective way to drive traffic to a SaaS business’s website, generate leads, and convert those leads into paying customers. By targeting specific keywords and demographics, SaaS businesses can ensure that their ads are seen by the right audience and maximize their chances of generating high-quality leads.
One of the critical advantages of PPC advertising is its ability to provide measurable results. By tracking metrics such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and cost-per-acquisition, SaaS businesses can gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of their PPC campaigns and make informed decisions about how to optimize those campaigns over time.
However, it’s important to note that PPC advertising can be expensive, especially in highly competitive industries. SaaS businesses should carefully manage their budgets and focus on targeting the right audience to ensure they get the best possible return on investment.
PPC advertising is a critical strategy for driving growth and success in the SaaS industry. By leveraging targeted ads and carefully tracking metrics, SaaS businesses can attract high-quality leads, increase conversions, and drive revenue growth over the long term.
Customer Lifecycle
The customer lifecycle is the series of stages a customer goes through, from initial awareness of a product or service to becoming a loyal, repeat customer. Understanding the customer lifecycle is critical for SaaS businesses, as it can help inform product development, sales and marketing strategies, and customer support efforts.
The customer lifecycle typically involves the following stages:
- Awareness: In the awareness stage, potential customers become aware of the product or service through marketing and advertising. This may include social media ads, blog posts, or other content marketing efforts.
- Acquisition: In the acquisition stage, potential customers become paying customers by signing up for a free trial or purchasing a subscription.
- Onboarding: In the onboarding stage, new customers are introduced to the product or service and provided with support and training to ensure their product is effective.
- Engagement: In the engagement stage, customers actively use the product or service and may provide feedback or engage with the company through customer support channels.
- Retention: In the retention stage, customers continue to use the product or service and may renew their subscriptions or make additional purchases.
- Advocacy: In the advocacy stage, loyal customers become advocates for the product or service, providing positive reviews, referrals, and recommendations to others.
By understanding the different stages of the customer lifecycle, SaaS businesses can develop targeted strategies for each step to retain customers and drive long-term growth and success.
This may involve providing effective onboarding and customer support, developing new features and updates to keep customers engaged, and offering incentives or promotions to encourage customer loyalty and advocacy.
The customer lifecycle is a critical concept for SaaS businesses, providing valuable insights into how customers interact with the product or service and how the company can maximize customer satisfaction and retention over the long term.

Customer acquisition and its importance in SaaS business growth
Customer acquisition is critical to driving growth and success in the SaaS industry. Acquiring new customers allows SaaS businesses to expand their user base, increase revenue, and achieve long-term profitability.
Effective customer acquisition strategies in the SaaS industry may involve a range of tactics, such as content marketing, social media advertising, email marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO). These tactics are designed to attract potential customers to the business and encourage them to sign up for a free trial or purchase a subscription.
The importance of customer acquisition in SaaS cannot be overstated. Without a steady flow of new customers, it is difficult for SaaS businesses to grow and succeed in the competitive marketplace. By acquiring new customers, SaaS businesses can increase their chances of converting those customers into paying customers, maximizing revenue potential, and achieving long-term success.
In addition, effective customer acquisition can help SaaS businesses identify and target their ideal customer profile, allowing them to focus their sales and marketing efforts more effectively. By understanding the needs and preferences of potential customers, SaaS businesses can tailor their messaging and campaigns to better resonate with those customers and drive higher conversion rates.
Customer acquisition is essential for driving growth and success in the SaaS industry. By prioritizing effective customer acquisition strategies and tactics, SaaS businesses can attract and engage potential customers, build brand awareness, and drive revenue growth and long-term success.
Customer onboarding and its role in driving customer success
Customer onboarding is critical to driving customer success in the SaaS industry. Onboarding involves introducing new customers to the product or service and providing them with the support and resources they need to be successful.
Effective customer onboarding can significantly impact customer satisfaction, retention, and revenue growth. By providing clear instructions and guidance, SaaS businesses can help new customers quickly understand the product or service’s value and use it effectively.
Some key strategies for effective customer onboarding in SaaS include:
- Providing clear instructions and tutorials: SaaS businesses should offer new customers step-by-step instructions and tutorials to help them get started with the product or service.
- Offering support and resources: SaaS businesses should provide new customers with access to customer support resources, such as a knowledge base or help desk, to ensure they have the support they need to succeed.
- Collecting feedback: SaaS businesses should collect feedback from new customers during onboarding to identify areas where the product or service can be improved and ensure that customers get the most value from the product or service.
Effective customer onboarding is critical for driving customer success in the SaaS industry. By providing new customers with the support and resources they need to be successful, SaaS businesses can increase customer satisfaction, retention, and, ultimately, revenue growth over the long term.
Customer retention and its impact on SaaS revenue growth
Customer retention is critical to driving revenue growth and long-term success in the SaaS industry. Retaining existing customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new customers, as it reduces churn and increases customer lifetime value.
Effective customer retention strategies in the SaaS industry may involve a range of tactics, such as providing excellent customer support, offering new features and updates, and providing incentives or discounts to encourage loyalty.
Some key strategies for effective customer retention in SaaS include:
- Providing excellent customer support: SaaS businesses should prioritize customer support, providing responsive and helpful support to address customer concerns and ensure satisfaction.
- Offering new features and updates: SaaS businesses should continue to develop and improve the product or service over time, providing customers with new features and updates that keep them engaged and interested.
- Providing incentives or discounts: SaaS businesses may offer incentives or discounts to customers who renew their subscriptions or make additional purchases, encouraging loyalty and repeat business.
Customer retention drives revenue growth and long-term success in the SaaS industry. By prioritizing effective customer retention strategies and tactics, SaaS businesses can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty, reduce churn, and ultimately achieve long-term profitability.

Pricing Strategies
Pricing strategies are a critical component of success in the SaaS industry. Effective pricing strategies can help SaaS businesses attract and retain customers, maximize revenue potential, and achieve long-term profitability.
There are several pricing strategies commonly used in the SaaS industry, including:
- Freemium pricing involves offering a free, limited version of the product or service, with the option to upgrade to a paid version with additional features and functionality.
- Tiered pricing: Tiered pricing involves offering multiple pricing tiers, each offering different levels of features and functionality at various price points.
- Usage-based pricing involves charging customers based on the number of products or services they use. This may be based on metrics such as several users or the amount of data storage.
- Value-based pricing: Value-based pricing involves pricing the product or service based on its perceived value to customers. This may include researching and analyzing customer needs and preferences to determine the price.
- Perpetual licensing: Perpetual licensing involves charging a one-time fee for the product or service, with the option to purchase additional upgrades or support services over time.
The choice of pricing strategy will depend on a range of factors, including the specific needs and preferences of the target market, the competition in the industry, and the overall revenue goals of the SaaS business.
By selecting the right pricing strategy and continually monitoring and adjusting pricing as needed, SaaS businesses can maximize their revenue potential and achieve long-term success.
Subscription pricing and variations
Subscription pricing is a popular pricing model in the SaaS industry, where customers pay a recurring fee to access the product or service over a set period. Subscription pricing can provide a predictable revenue stream for SaaS businesses and encourage customer loyalty and repeat business.
There are several variations of subscription pricing commonly used in the SaaS industry, including:
- Monthly subscription: Monthly subscription pricing involves charging customers a fixed monthly fee to access the product or service.
- Annual subscription: Annual subscription pricing involves charging customers a fixed fee for a full year of access to the product or service. Annual subscriptions may be offered at a discounted rate compared to monthly subscriptions.
- Multi-year subscription: Multi-year subscription pricing offers customers a discounted rate for committing to a more extended subscription period, such as two or three years.
- Pay-as-you-go subscription: Pay-as-you-go subscription pricing involves charging customers based on usage, with customers paying only for the product or service they use.
- Per-user pricing: Per-user pricing involves charging customers based on the number of users accessing the product or service. This may include offering different pricing tiers based on the number of users.
The choice of subscription pricing variation will depend on a range of factors, including the specific needs and preferences of the target market, the industry’s competition, and the SaaS business’s overall revenue goals.
By selecting the correct subscription pricing model and continually monitoring and adjusting pricing as needed, SaaS businesses can maximize their revenue potential and achieve long-term success.
Usage-based pricing: Advantages and Disadvantages
Usage-based pricing is a pricing model where customers are charged based on the number of products or services they use. This model is commonly used in the SaaS industry, particularly for variable usage products or services.
Advantages of usage-based pricing include:
- Flexibility: Usage-based pricing allows customers to pay only for what they use. This can be particularly appealing for customers with variable usage levels or who may only need the product or service sometimes.
- Fairness: Usage-based pricing is often seen as fair, as customers only pay for the amount of product or service they use. This can appeal to customers needing to spend more with flat-rate pricing models.
- Scalability: Usage-based pricing can be scalable, allowing SaaS businesses to grow revenue as usage levels increase. This can be particularly appealing for proliferating companies with a large customer base.
However, there are also some potential disadvantages of usage-based pricing, including: - Complexity: Usage-based pricing can be complex to manage, particularly for businesses with large or variable customer bases. This can make it difficult to track usage levels and bill customers accordingly accurately.
- Uncertainty: Usage-based pricing can create tension for customers, as they may need to know exactly how much they will be charged monthly. This can be particularly challenging for customers with tight budgets or limited cash flow.
- Incentives: Usage-based pricing can incentivize customers to use the product or service less, reducing costs. This can be particularly challenging for businesses that rely on high usage levels to generate revenue.
Usage-based pricing can be effective for SaaS businesses, particularly products or services with variable usage levels. However, companies should carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of this pricing model and determine whether it is the best fit for their specific needs and target market.
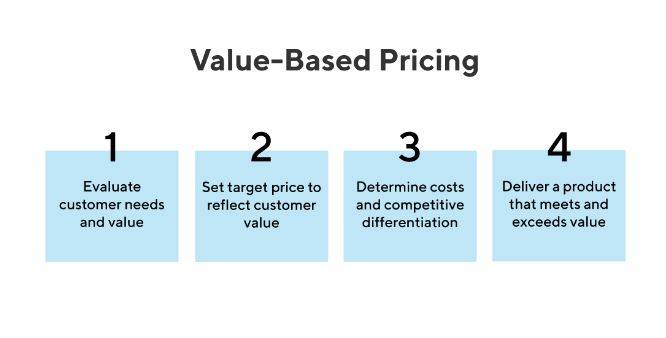
Value-based pricing and pricing SaaS offerings
Value-based pricing is a pricing model that involves setting prices based on the perceived value that the product or service provides to customers. In the SaaS industry, value-based pricing can maximize revenue potential and encourage customer loyalty.
To implement value-based pricing for SaaS offerings, businesses should start by understanding the needs and preferences of their target market. This may involve conducting market research, analyzing customer data, and identifying key pain points or challenges the product or service can help solve.
Once the business understands the value the product or service provides customers, it can determine an appropriate price point based on that value. This may involve offering different pricing tiers based on the level of the value supplied or offering premium features or services at a higher price point.
When pricing SaaS offerings, businesses should also consider the competition in the industry, as well as the overall revenue goals of the company. Pricing should be competitive and aligned with the product or service’s value while maximizing long-term revenue potential.
Value-based pricing can be effective for SaaS businesses, particularly for products or services that provide significant customer value. By understanding the needs and preferences of the target market and setting prices based on the perceived value provided, SaaS businesses can maximize revenue potential, encourage customer loyalty, and achieve long-term success.
Technical Terminology
API and its role in SaaS integration
API stands for Application Programming Interface, a set of protocols, routines, and tools for building software applications. In the context of SaaS integration, APIs play a critical role in enabling different software systems to communicate and share data.
APIs allow SaaS businesses to integrate their products or services with other software systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM), project management tools, and accounting software. Integrating with other software systems allows SaaS businesses to improve efficiency, streamline workflows, and enhance overall functionality.
APIs enable SaaS businesses to expose their data and functionality to third-party developers, who can build their applications on the existing SaaS platform. This can lead to a more robust and diverse software application ecosystem, increasing the SaaS platform’s overall value for users.
In addition, APIs can help SaaS businesses reduce development costs and accelerate time-to-market for new features and functionality. By providing a standard interface for software integration, APIs can simplify the development process and enable more rapid iteration and deployment of new features and updates.
APIs are critical in enabling SaaS integration and driving innovation and growth in the SaaS industry. By leveraging APIs effectively, SaaS businesses can enhance their functionality, improve efficiency, and deliver more value to their customers.
Scalability and SaaS technology infrastructure
Scalability refers to the ability of a system or infrastructure to handle increasing workloads and demands without sacrificing performance or functionality. In the context of SaaS technology infrastructure, scalability is critical for enabling SaaS businesses to grow and expand their user base without encountering performance or capacity issues.
Adequate SaaS technology infrastructure should be designed to be highly scalable and able to handle increasing workloads and demands as the business grows. This may involve using cloud-based infrastructure, such as Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure, that can scale up or down to meet changing demand.
Some key strategies for building a scalable SaaS technology infrastructure include:
- Horizontal scaling involves adding more servers or resources to handle increasing demand. This can be achieved through techniques such as load balancing and clustering.
- Auto-scaling: Auto-scaling involves automatically scaling resources up or down based on changing demand. This can be achieved using cloud-based infrastructure and technologies such as Kubernetes.
- Flexible architecture: Elastic architecture involves designing the infrastructure to be flexible and adaptable, able to handle changing workloads and demands without sacrificing performance or functionality.
Scalability is essential for SaaS businesses looking to grow and expand their user base over the long term. By building a highly scalable SaaS technology infrastructure, companies can ensure that they can handle increasing demand and deliver a high-quality user experience, even as the business continues to grow and evolve.

Data security and protecting customer data
Data security is critical for SaaS businesses, particularly as more sensitive data is stored and processed in the cloud. Protecting customer data is a legal and ethical obligation for SaaS businesses and essential for maintaining customer trust and loyalty.
To protect customer data, SaaS businesses should implement a range of security measures and best practices, including:
- Encryption: Encryption involves encoding data to prevent unauthorized access. SaaS businesses should use robust encryption protocols to protect sensitive customer data, such as personal and financial data.
- Access controls: Access controls limit customer data access to authorized personnel only. SaaS businesses should implement strong authentication and authorization procedures to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
- Regular backups: Regular backups are critical for ensuring that customer data can be restored in the case of a security breach or data loss. SaaS businesses should implement routine backup procedures to protect customer data.
- Data monitoring and logging: Data monitoring involves access and usage to identify potential security threats. SaaS businesses should implement robust data monitoring and logging procedures to detect and respond to potential security threats.
Protecting customer data is essential for maintaining customer trust and loyalty in the SaaS industry. By implementing strong data security measures and best practices, SaaS businesses can ensure that customer data is safe and secure and that customers feel confident using the product or service over the long term.
Conclusion
Final thoughts and recommendations
In conclusion, the SaaS industry is a rapidly growing and dynamic field, with many opportunities for businesses looking to build successful SaaS products or services. Business companies prioritize compelling SaaS fundamentals, business metrics, sales and marketing, customer lifecycle management, pricing strategies, and technical infrastructure to succeed in the SaaS industry.
Some key recommendations for businesses looking to succeed in the SaaS industry include:
- Focus on customer needs and preferences: SaaS businesses should prioritize understanding the needs and preferences of their target market and building products or services that meet those needs effectively.
- Embrace a data-driven approach: SaaS businesses should leverage data and analytics to make informed decisions and optimize performance over time.
- Prioritize customer experience: SaaS businesses should prioritize delivering a high-quality customer experience, providing excellent customer support, and continuously improving the product or service over time.
- Invest in effective marketing and sales strategies: SaaS businesses should invest in effective marketing and sales strategies to drive customer acquisition and retention and maximize revenue potential over the long term.
- Build a scalable and secure technical infrastructure: SaaS businesses should build a highly scalable and secure technical infrastructure, able to handle increasing workloads and demands without sacrificing performance or functionality.
The SaaS industry offers many opportunities for businesses looking for successful and sustainable products or services. By prioritizing effective strategies and best practices, business companies achieve long-term growth and success in this dynamic and exciting field.

FAQs
What are SaaS and h, and how is it different from traditional software models?
SaaS stands for Software as a Service, and it is a software delivery model in which software is hosted on the cloud and made available to users via a subscription-based model. SaaS is different from traditional software models in several key ways.
- Firstly, SaaS is typically accessed via the internet rather than installed on individual devices. This means that users can access the software from anywhere with an internet connection, making it more flexible and accessible than traditional software models.
- Secondly, SaaS is typically offered on a subscription-based model, with users paying a recurring fee for access to the software. This differs from traditional software models, which are usually a one-time purchase of software purchase with ongoing costs.
- Thirdly, SaaS is the software provider that typically maintains and updates SaaS than the user. Users do not need to worry about software maintenance or updates, as the provider handles these automatically.
- Finally, SaaS is often more scalable and flexible than traditional software models, able to handle increasing workloads and demands without sacrificing performance or functionality. This is because SaaS is typically hosted on cloud-based infrastructure, which can scale up or down as needed to meet changing demand.
SaaS offers many advantages over traditional software models, including greater flexibility, accessibility, and scalability. By embracing SaaS, businesses can deliver more value to their customers and achieve long-term success in a rapidly changing and dynamic market.
What are the key SaaS business metrics, and why are they important?
Several key business metrics are critical for SaaS businesses to track and analyze. These metrics provide valuable insights into the health and performance of the company and help inform strategic decision-making over the long term.
Some of the key SaaS business metrics include:
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): MRR is the revenue a SaaS business generates monthly from its subscription-based model. MRR is critical for understanding the company’s overall revenue performance and can help inform pricing and revenue optimization strategies over time.
- Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR): ARR is similar to MRR, but it provides a snapshot of the annual revenue generated by a business, is helpful and valuable for measuring the growth and success of the company over time, and can help inform long-term strategic planning.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): CAC is the amount of money as spends to acquire each new customer. This metric is crucial in understanding the overall cost of customer acquisition and helps inform marketing and sales strategies over time.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): CLV is the total revenue expected to generate over their relationship with the business. CLV is helpful and valuable for understanding the overall value of the customer base, and it help informs customer retention and loyalty strategies over time.
- Churn Rate: The churn is when customers cancel their subscriptions or stop using the product or service. Churn rate is a critical metric for understanding customer retention and loyalty, and it helps inform product and service improvements over time.
These key SaaS business metrics provide valuable insights into the health and performance of the business and help inform strategic decision-making over the long term.
By tracking and analyzing these metrics effectively, SaaS businesses can optimize performance, improve customer acquisition and retention, and achieve long-term success in a rapidly changing and dynamic market.
What is the sales funnel, and how does it work in SaaS?
The sales funnel, or the marketing funnel, represents a potential customer’s journey from initial awareness of a product or service to the final purchase. The horn is chronically divided into several stages, each presenting a different level of engagement and commitment from the customer.
In the context of SaaS, the sales funnel typically involves several key stages:
- Awareness: The first stage of the funnel involves creating awareness of the product or service among potential customers. This may include marketing and advertising campaigns, content marketing, and social media outreach.
- Interest: The next stage of the funnel involves generating interest among potential customers. This may include providing free trials or demos of the product or service and offering valuable content and resources to educate potential customers about the product or service.
- Evaluation: The evaluation stage involves potential customers evaluating the product or service and comparing it to other options on the market. This may include providing detailed product information, case studies, and customer reviews to help potential customers make informed decisions.
- Purchase: The purchase stage involves the customer purchasing the product or service. This may include pricing information, customer support, and other resources to help facilitate the purchase process.
- Retention: The final stage of the funnel involves retaining the customer over the long term through ongoing support, communication, and engagement. This may include providing regular updates and improvements to the product or service and offering ongoing customer support and resources.
The sales funnel provides a framework for understanding and optimizing the customer journey in the context of SaaS.
By understanding the critical stages of the funnel and developing effective strategies to engage and convert potential customers at each location, SaaS businesses can optimize performance, improve customer acquisition and retention, and achieve long-term success in a rapidly changing and dynamic market.

What are the different pricing strategies for SaaS offerings?
SaaS businesses have several different pricing strategies, depending on their specific needs and goals. Here are some of the most common pricing strategies for SaaS offerings:
- Subscription pricing: Subscription pricing is the most common pricing model for SaaS businesses. Under this model, customers pay a recurring fee (usually monthly or annually) for access to the software or service.
- Usage-based pricing involves charging customers based on how much they use the software or service. This model is prevalent in industries such as cloud computing, where customers pay for the resources they use.
- Freemium pricing: Freemium pricing involves offering a free basic version of the software or service with more advanced features for a fee. This model is particularly effective for SaaS businesses looking to quickly acquire a large user base.
- Tiered pricing involves offering multiple pricing tiers with different features and functionality at each level. This model is particularly effective for SaaS businesses targeting different customer segments with different needs and budgets.
- Value-based pricing: Value-based pricing involves setting prices based on the software or service’s value to the customer. This model is particularly effective for SaaS businesses offering specialized or niche products or services.
SaaS businesses should choose a pricing strategy that aligns with their specific needs and goals and effectively communicates the value of the software or service to potential customers.
By developing an effective pricing strategy, SaaS businesses can optimize revenue, attract and retain customers, and achieve long-term success in a dynamic and competitive market.
What is API, and why is it essential in SaaS integration?
API stands for Application Programming Interface, a set of protocols and tools that enable different software applications to communicate with each other. In the context of SaaS, APIs are critical for integrating various software applications and systems, allowing data to be shared and exchanged seamlessly across different platforms.
APIs are essential in SaaS integration for several important reasons.
- Firstly, APIs enable different software applications to communicate with each other standardized and consistently. SaaS businesses can integrate with other software applications quickly and easily without extensive custom coding or manual data entry.
- Secondly, APIs enable SaaS businesses to offer their customers robust and flexible integration capabilities. By exposing APIs to customers, SaaS businesses can allow their customers to integrate with other software applications and systems, creating a more seamless and integrated user experience.
- Finally, APIs can help SaaS businesses to unlock new revenue streams and business models. By exposing APIs to third-party developers, SaaS businesses can enable the creation of new applications and services that integrate with their platform, creating new opportunities for revenue and growth.
APIs are critical for enabling seamless and flexible integration between different software applications and systems in the context of SaaS. By embracing APIs and developing effective API strategies, SaaS businesses can unlock new opportunities for revenue, growth, and innovation over the long term.
- Success vs. Significance: Understanding the Difference and Achieving Both - October 1, 2023
- 8 Steps to SaaS Success: From Idea to Business - September 30, 2023
- The Importance of Testing in SaaS: Ensure Quality and Success - September 29, 2023